Octal Converter: The 3-Bit Classic
Created on 9 November, 2025 • Converter Tools • 0 views
Work confidently with octal—convert between octal, decimal, binary, and hex. Understand Unix permission modes, 3-bit groupings, and common pitfalls.
Why Octal Still Matters
Octal (base-8) shines where 3-bit groupings are natural. It’s famous for Unix permission modes (0755, 0644) and appears in embedded/legacy systems. An octal converter helps you move cleanly between octal, decimal, binary, and hex.
Conversions at a Glance
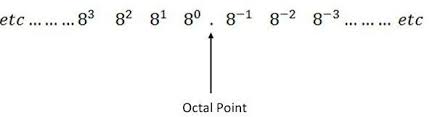
Octal ↔ Decimal
- Each octal digit represents powers of 8.
0755(octal) → decimal by7×8² + 5×8¹ + 5×8⁰.
Octal ↔ Binary
- Group binary in threes:
111 101 101→7 5 5. - This makes permission bits easy to read (
rwxmaps to111).
Octal ↔ Hex
- Convert via binary: octal → binary (3-bit groups) → hex (4-bit groups).
Unix Permissions Demystified
Interpreting 0755
- The leading
0or0omarks octal. 7=rwx(owner),5=r-x(group),5=r-x(others).- Special bits (setuid, setgid, sticky) appear as an extra leading octal digit.
Best Practices and Pitfalls
- Keep the leading zero when octal is required (
0755, not755). - Validate ranges: each octal digit must be
0–7. - Don’t mix file permission semantics with ACLs—some systems extend beyond simple octal.
Popular posts
-
Old English Text GeneratorText tools • 30 views
-
Cursive Text GeneratorText tools • 28 views
-
DNS Lookup ToolChecker Tools • 27 views
-
Reverse IP LookupChecker Tools • 26 views
-
Whois LookupChecker Tools • 26 views